Let us face it, for millions of people, student loans play a significant role in their lives. That debt-to-income (DTI) ratio, however, becomes crucial when it comes time to buy a home, obtain a car loan, or simply breathe financial air. Knowing this figure can be the game-changer you did not know you needed, regardless of how long you have been in debt, whether you are just out of college or ten years in.
What Is a Debt-to-Income (DTI) Ratio?
A straightforward formula that indicates the percentage of your monthly income that is used for debt repayment is the DTI ratio. Lenders use this proportion to determine how risky it would be to give you a loan. The greater the ratio, the larger the portion of your income that is consumed by debt, including student loans.
Why the DTI Ratio Matters for Student Loan Borrowers
Your DTI has the power to either open doors or close them. Do you wish to obtain a mortgage? Do you require a vehicle loan? Before approving your loan, lenders review your DTI. Even if you have excellent credit, you may be refused if student loans are driving up your ratio too much. For this reason, knowing your ratio is essential to achieving financial independence.
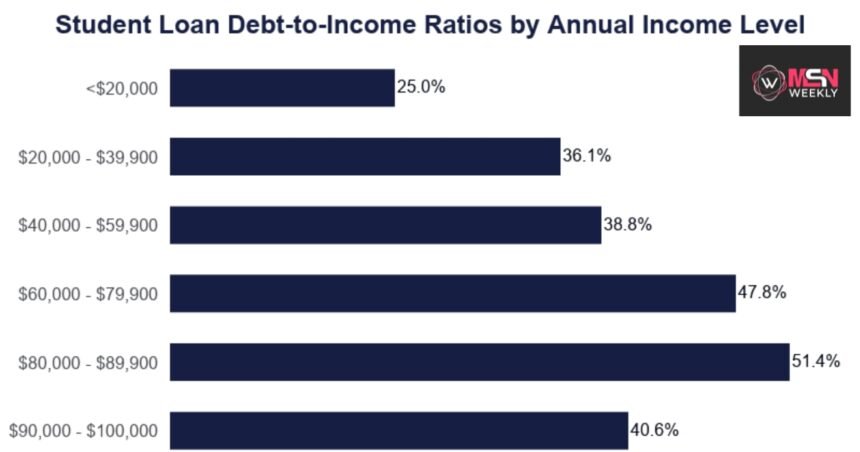
“Student Loans Debt to Income Ratio”
Front-End vs. Back-End DTI
There are two flavors of DTI:
-
Front-End DTI only includes housing costs (rent, mortgage, taxes).
-
Back-End DTI includes all debts—student loans, credit cards, car loans, etc.
A Step-by-Step DTI Calculation Example
Here’s how you calculate your back-end DTI:
-
Add up your monthly debt payments.
Example:-
Student loans: $300
-
Car loan: $250
-
Credit card minimum: $150
-
Total = $700
-
-
Determine your gross monthly income (before taxes).
Example: $3,500 -
Divide debt by income:
$700 ÷ $3,500 = 0.20 -
Multiply by 100 to get a percentage:
0.20 × 100 = 20% DTI
What’s a Good DTI Ratio When You Have Student Loans?
Generally speaking, a DTI below 36% is seen as healthy. Less than 20%? That is great. However, you are in risk, especially when it comes to mortgages, if your DTI is higher than 43%. It is time to reconsider your repayment plan if student loans are the primary cause.
How Student Loans Affect Your DTI
Private versus Federal Student Loans
Income-driven repayment (IDR) programs are commonly available for federal loans, and they can reduce your monthly payments. Individual loans? Not really—lenders demand standard payments and are less accommodating, which can quickly raise your DTI.
Income-Driven Repayment Plans’ Effects
Lenders may calculate DTI using your actual payment rather than the usual one if you are on an IDR plan. However, if they are unable to verify your payment, some mortgage lenders continue to apply the 1% rule, which is equal to 1% of your entire loan sum. Your DTI may appear higher than it actually is as a result.
How Lenders Use DTI to Evaluate You
DTI in Mortgage Approval
When it comes to DTI, mortgage lenders are stringent. Many adhere to the 28/36 rule, which states:
Housing should not exceed 28% of income.
36% or less of total debt
This can be impacted by student loans, which might make qualifying more difficult.
DTI for Auto or Personal Loans
Credit card firms and auto lenders are a bit more accommodating. Still, a high DTI is cause for concern. They want to confirm that you can manage additional debt without going bankrupt.
Strategies to Improve Your DTI Ratio
Boosting Income
It should go without saying: increase your income! It may be easier said than done, but you can increase your income by taking on side jobs, freelancing, or requesting a raise.
Reducing Debt
Pay off credit cards or loans with high interest rates first. To assault your balance and pull that DTI down, use the avalanche or snowball strategy.
Consolidating or refinancing student loans
Refinance your student loans for a lower interest rate and smaller monthly payment if your credit score is good. Your DTI ratio will immediately improve as a result.
Student Loan Forgiveness and Its Effect on DTI
Congratulations if you are eligible for student loan forgiveness; it can greatly reduce your debt load. It reduces the amount that lenders take into account when determining your DTI, whether it is through income-driven plan forgiveness or Public Service Loan Forgiveness (PSLF).
Final Thoughts on Managing Your Student Loan DTI Ratio
Your DTI ratio isn’t just a number—it’s a reflection of your financial flexibility. Understanding how student loans affect it puts you in control. With the right mix of strategy, awareness, and maybe a little hustle, you can make your DTI ratio work for you instead of against you.